COLD Feature Based Handwriting Analysis for Ethnicity Identification
July 25, 2019
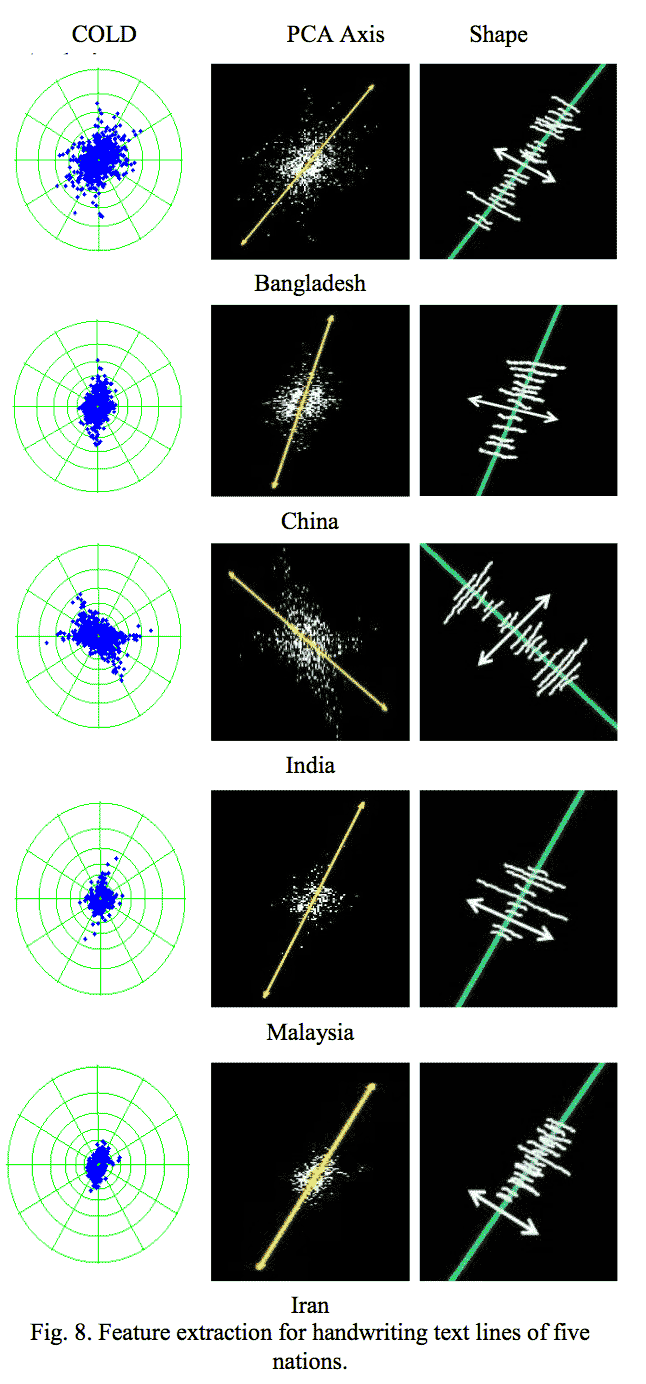
Different Cloud of Line (COLD) distributions of writers from different nationalities. Traits, namely, gender, nationality, age, height, gait,etc.,are popular in the field of biometric applications, such as faceand iris recognition[1, 2]. This is because traits prediction helpsbiometric methods to improve their performancesby reducing the complexity of the problem [3, 4]. In addition, traits prediction plays a vital role for forensic applicationsand securitybyhelping in identifying suspicious behaviors[1]. However, it is noted from biometric based methods that when the input images are posed to an open environment, the methods lose accuracy. This is due to inherent limitations of biometric based methods, such as sensitivity to non-uniform illuminationeffect, occlusion, degradation, and environmentinfluences. Besides, the methods are said to be computationally expensive as it involves high-levelimage processing tasks. As a result, in order to help forensic applicationsand investigation teams, handwriting analysis has received a special attention of the researchers,which has now reached beyond traditional boundaries such as emotions nationality, gender, age and other traits prediction [4, 5]. However, due to large variations in handwriting, ink, pen, paper, script, age, gender, and individual difference, it is not so easy to identify traits based on handwriting analysis accurately. Therefore, this work focuseson nationality and ethnicity identification asit is useful for identifying crimeswhere different nationalsare involved. Despite the problem is challenging as mentioned above, one can expect differences in writing styles of different nationals. For example, Chinese usually prefer to write letters with more straight than cursive. This is valid because of the nature of their national language,where alphabets and text usually are formed with the combination of straight strokes. Incase of people originating from Indiaand Bangladesh, we can expect more cursivethan straightness compared to Chinese because most of Indian and Bangladesh scripts are cursive in nature. With this notion, one can confirm that English writing changes from one national to another. This is the main basis for proposing the method in this work. It is evident from thesample images of each nation shown in Fig. 1,where it can be seen that each nation has a different writing style. At the same time, since all the citizens of respective nations follow their own scripts, we can expect English writing by different persons of the same nation share the common properties
Source: Nag, Sauradip, et al. "New COLD Feature Based Handwriting Analysis for Enthnicity/Nationality Identification." 2018 16th International Conference on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR). IEEE, 2018.
Source URL: https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.07072
ID: cold-feature-based-handwriting-analysis-for-ethnicity-identification
Categories:
Tags: Boerhaave | COGWEB | Chinese | LSTM | Leiden | PGM | RNN | Ruysch | actors | aesthesis | agency | algorithm | analysis | anatomical | anatomy | androgynous | architecture | archive | artificialia | axis | black-box | body | botanical | brain | categories | categorization | channel | character recognition | chinese | classification | clustering | cnn | codes | cognition | collecting | collection | collections | colonialism | commodification | concept | conceptual-clustering | convolutional neural network | cost | counting | cut | cuts | cutting | datasets | demonstration | diagram | dimensionality | disgust | dissection | distance | domestication | elegance | epistemology | error | euclidean | evaluation | eye | figures | finger | forecasting | forensics | frame | freakish | geometry | gesture | gestures | gradient descent | graph | graphs | grouping | hacking | hand | hand writing | hands | hands-on | handwriting | hardware | history | human | human body | imagination | imperfect | inscription | instruments | joint | kmeans | knowledge | labeling | landmark | learning | location | machine learning | machines | materiality | meaning | measurement | memory | mnist | model | models | monsters | muscles | mystical | mythological | naturalia | nerves | nervous system | network | networks | neural networks | neural-anatomy | neuron | nonlinearity | observation | offline | online | ontologies | ontology | ontology-building | optimization | orientation | orthogonality | parallel | pca | perception | perceptron | perfection | performance | planes | poetic | position | prediction | preparation | preparations | projection | proportion | proportions | psychology | python | races | representation | representations | rhetoric | rnn | segments | selection | sensory experience | sensory perception | similarity | skeleton | skin | skull | skulls | space | sparseness | spectacle | spectators | speech | standard | statistic-ontology | statistical | statistical-ontology | svm | symbols | tacit | taxonomy | theatre | time-series | timeseries | tools | topological | training | treatise | trial | truth | type | typography | unsupervised | vision | visualization | wellcome | word2vec | writing | zodiac |